LIST
PRODUCTS
Contact us
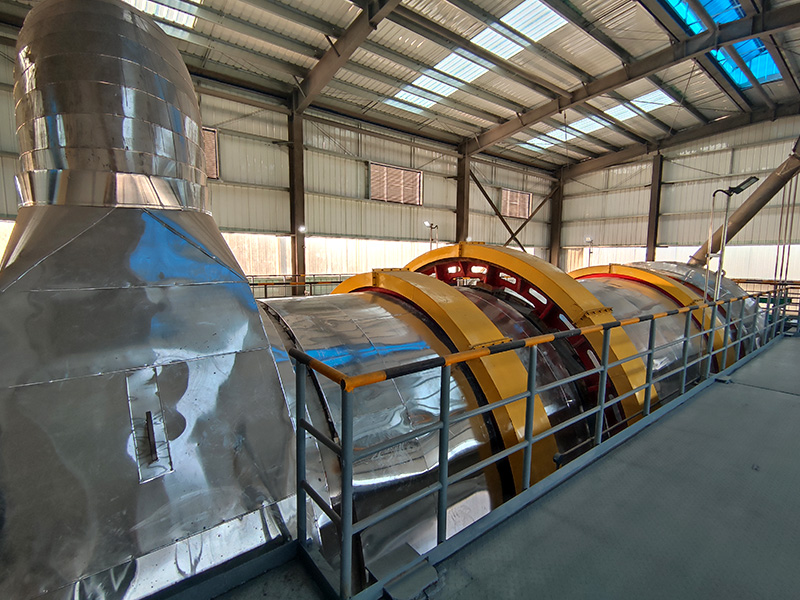
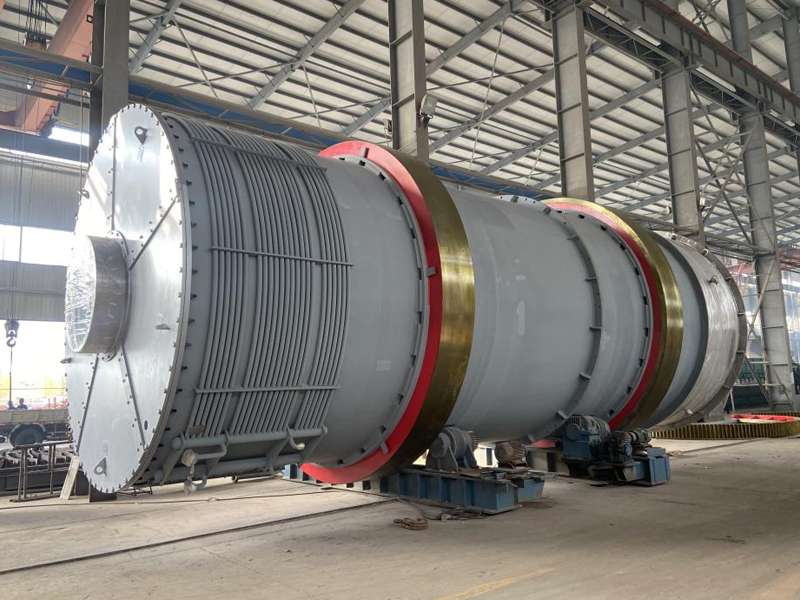
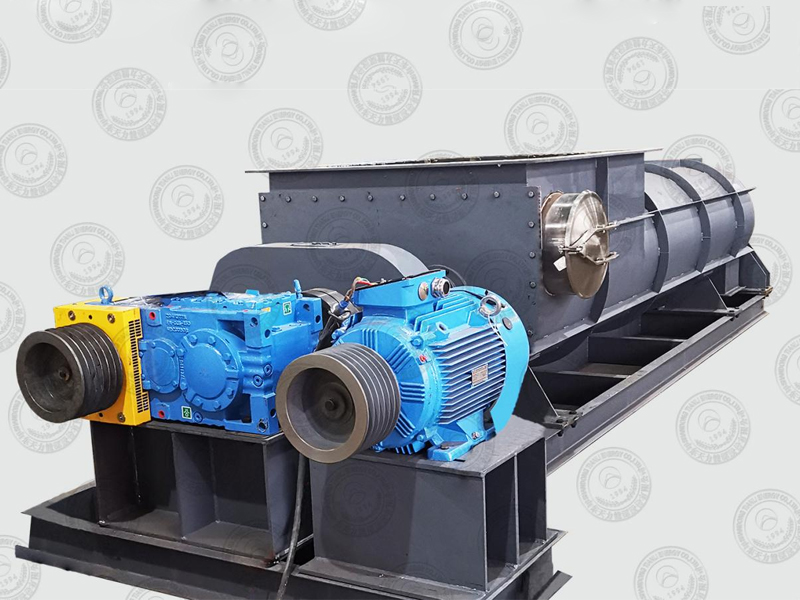
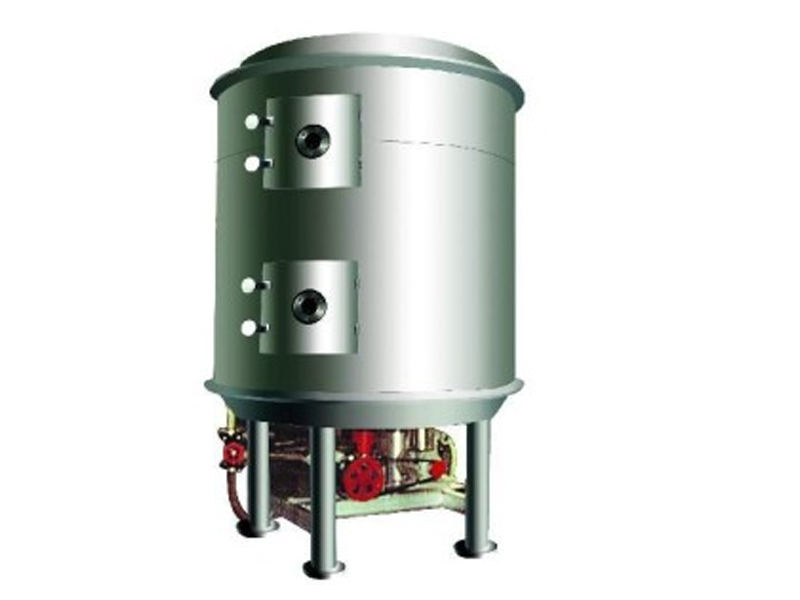
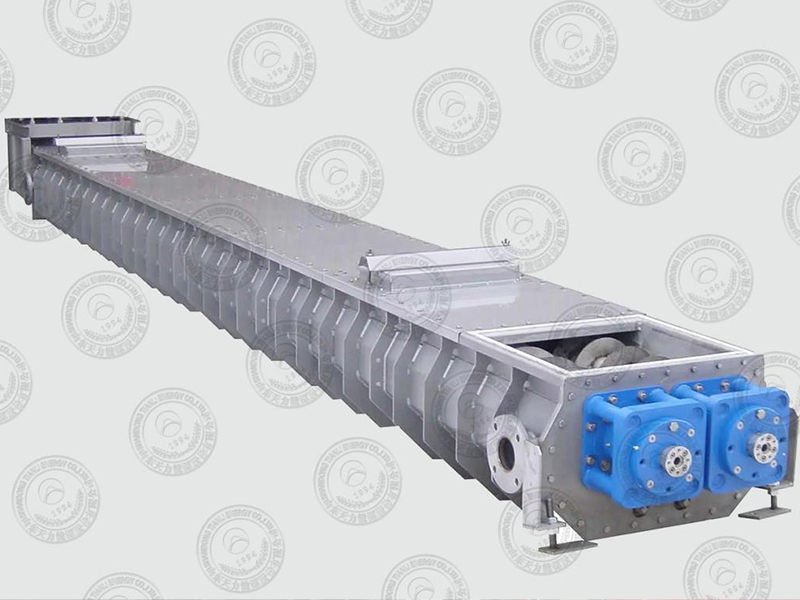
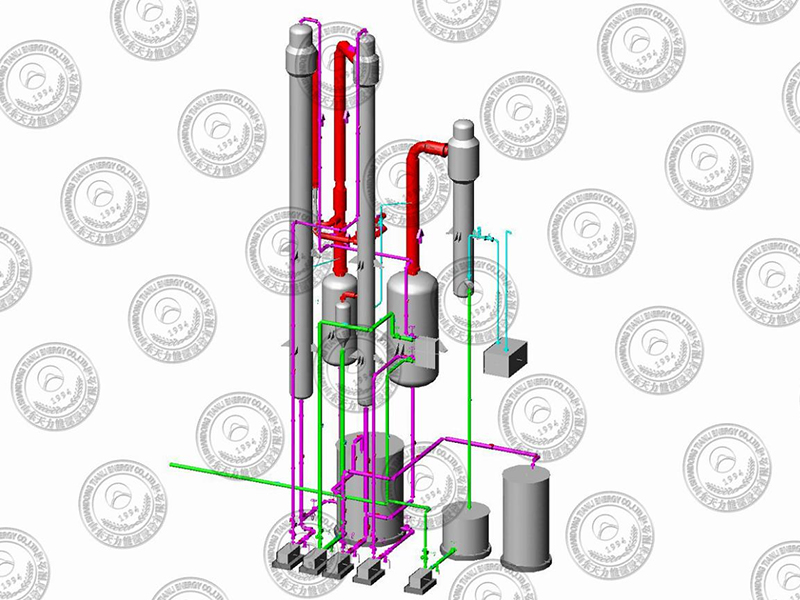
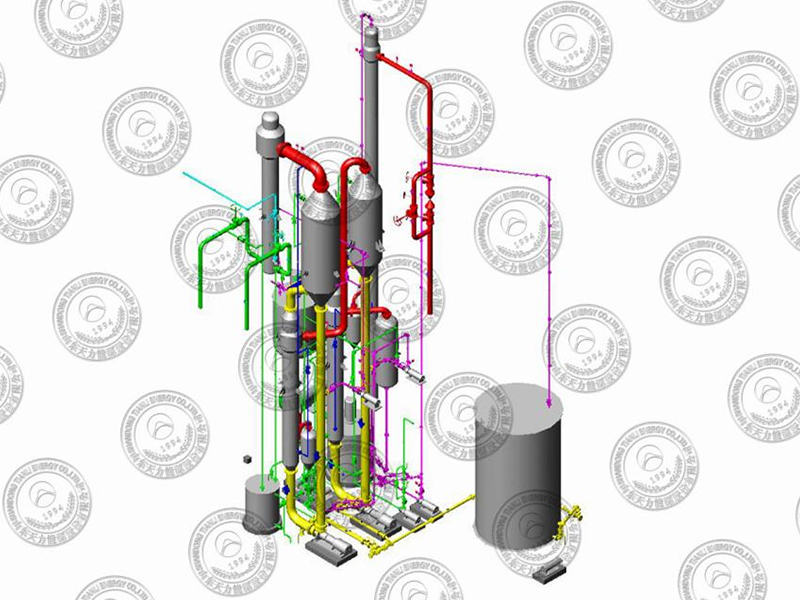
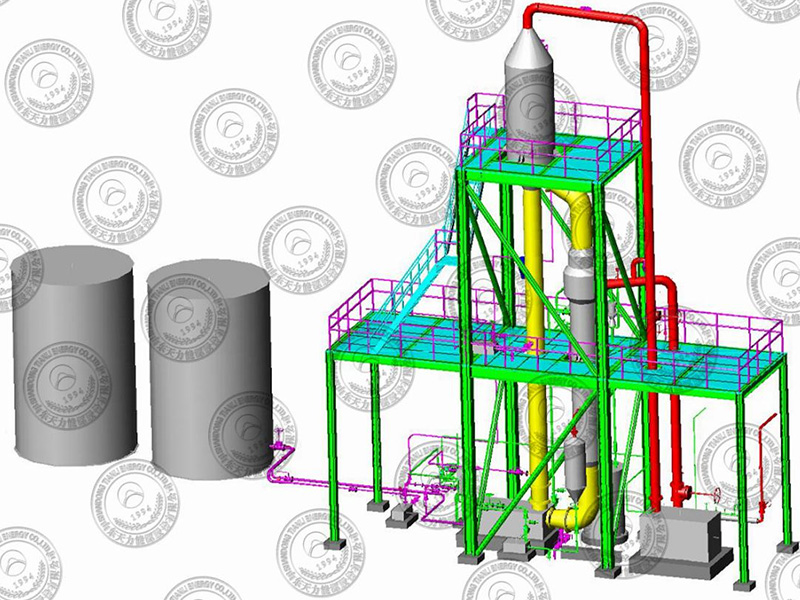
Disc Dryer
- Tianli
- China
Working Principle Diagram Of Dryer
Working Principle Diagram Of Dryer
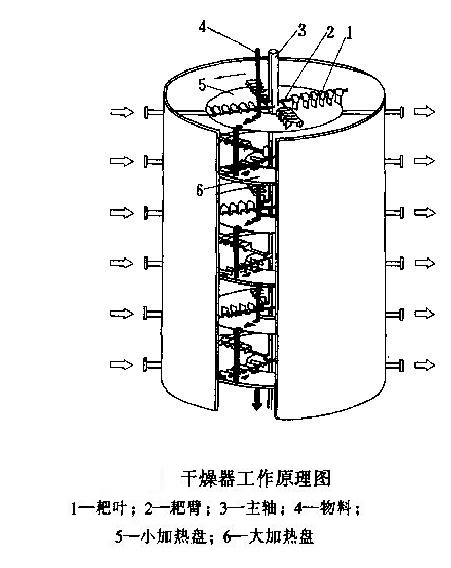
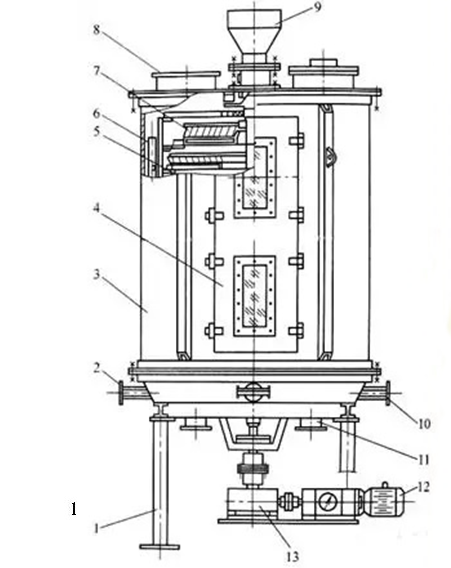
Rake Blade
Rake Arm
Main Shaft
Material
Small Heating Plate
Large Heating Plate
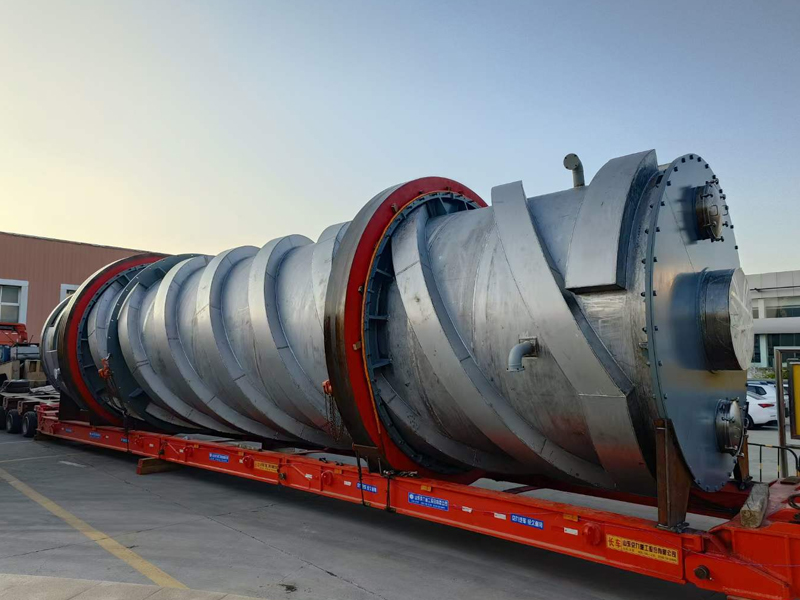
Disc dryer is a continuous drying equipment with multiple layers of horizontal discs. Each disc is equipped with a heating device. The material is pushed by rakes on the disc surface and dries in contact with the hot surface. It has high thermal efficiency and low energy consumption. It is suitable for paste, granular, powder and other materials. The drying degree can be controlled by adjusting the speed and temperature. It is easy to operate and takes up little space.
Structure And Composition
The disc dryer is a highly efficient conduction-type continuous drying equipment, mainly composed of the following core components:
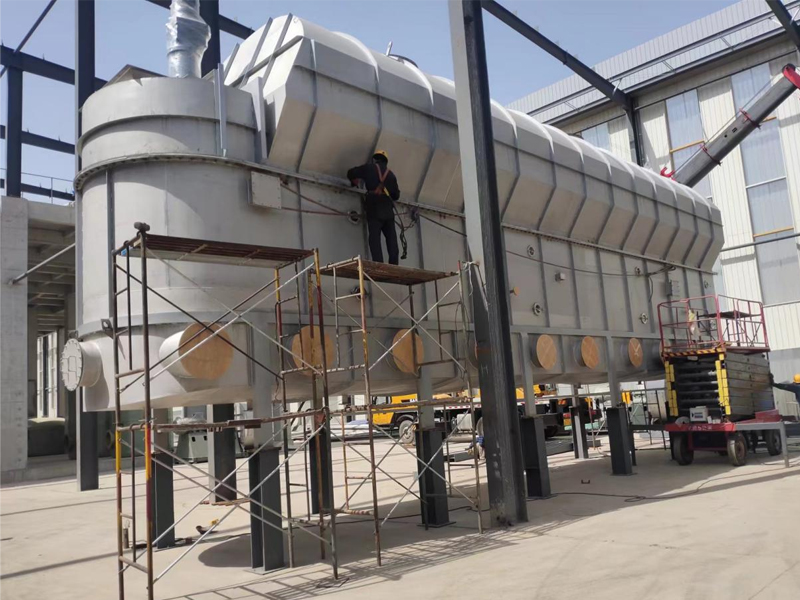
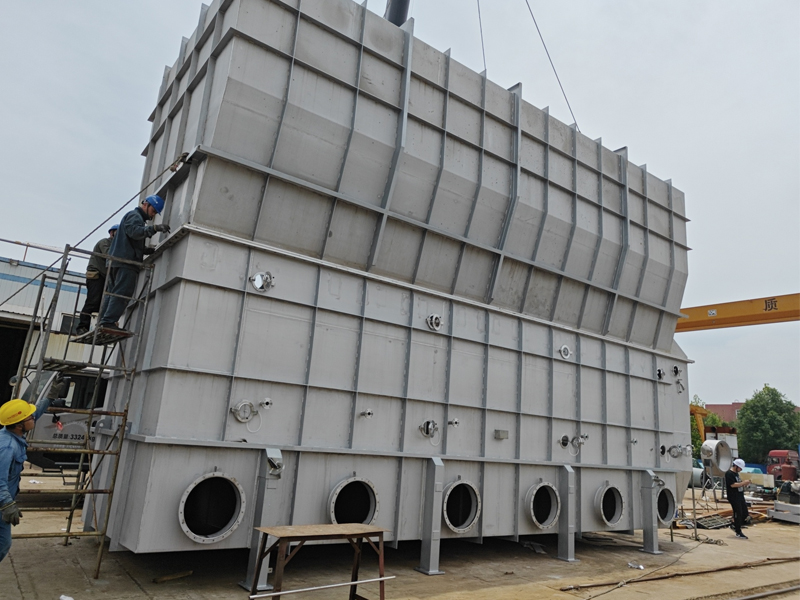
Main frame:
a. Shell: normal pressure, closed or vacuum design, providing a dry environment.
b. Frame: supports the entire equipment structure and ensures operational stability.
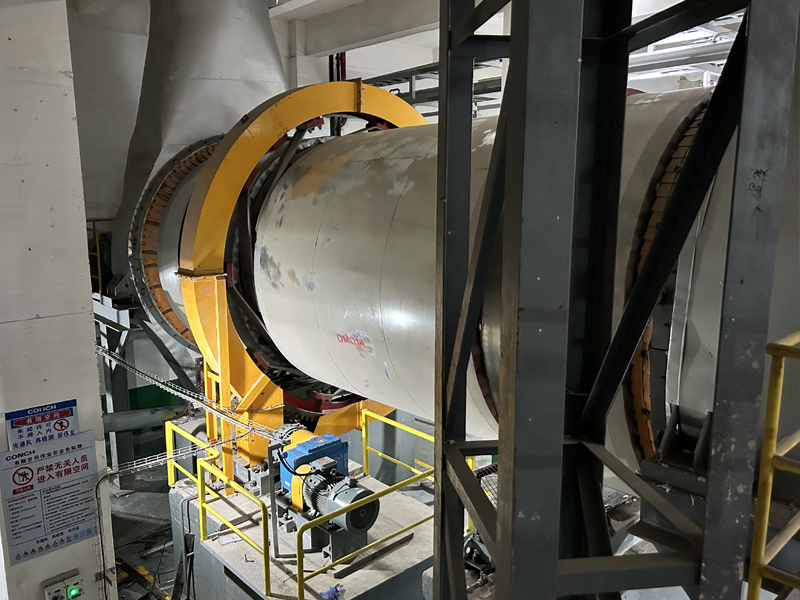
Heating system:
a. Multi-layer hollow heating plate: large/small plates are arranged alternately, and heating medium (steam, hot water or heat transfer oil) is passed inside.
b. Heating medium pipeline: distributed inside the drying plate to ensure uniform heat conduction.
Transmission system:
a. Main shaft: drives the rake arm to rotate, the speed is usually 1-10 rpm (stepless speed regulation).
b. Rake arm and rake blade: continuously turn the material to ensure uniform heating, and the gap between the rake blade and the plate surface is adjustable.
c. Drive device: includes motor, reducer and speed control box.
Auxiliary system:
a. Feeder: spiral or vibration type, to achieve continuous and uniform feeding.
b. Discharging device: bottom discharge port cooperates with conveying equipment.
c. Vacuum system (vacuum type): including vacuum pump and condensing device.
d.Dust removal system: handles dust generated during the drying process.
Working Principle
Material movement path:
a. Wet materials are added to the first layer of small drying plate from the top.
b. Rakes push materials along the spiral line to the outer edge → fall into the outer edge of the large drying plate below.
c. Materials on the large drying plate move toward the center → enter the next layer of small drying plate through the drop port.
d. After multiple layers of alternating drying, the finished product is discharged from the bottom layer.
Heat and mass transfer mechanism
a. Heat is transferred to the material through the drying plate to evaporate moisture.
b. Moisture escapes from the material and is discharged through the top moisture outlet or vacuum outlet.
c. Material residence time is 5-80 minutes, which can be adjusted by the spindle speed.
Core Advantages
High thermal efficiency: heat conduction directly acts on the material, with little heat loss, and the thermal efficiency can reach 70%-90%, which is 30%-50% more energy-efficient than traditional convection drying.
Small footprint: the multi-layer discs are arranged vertically, the drying area is concentrated, and the drying efficiency per unit area is high, which is suitable for scenes with limited space.
Strong material adaptability: it can handle heat-sensitive, easy-to-agglomerate, and high-viscosity materials, and the drying temperature is low to avoid high-temperature denaturation of the material.
Low pollution and low energy consumption: the closed structure reduces dust leakage and reduces waste gas emissions; the heating medium is recycled, with low energy consumption, which meets environmental protection requirements.
Stable and controllable operation: the drying process is continuous, and the moisture content of the product can be accurately controlled by adjusting the heating temperature, stirring speed, and material residence time, with a high degree of automation.
Applicable Materials
Disc dryers are suitable for the following types of materials, especially those that require low-temperature drying or are easily damaged:
Chemical industry: inorganic salts, pigments, dye intermediates, catalyst carriers, plastic additives, etc;
Food and medicine: heat-sensitive materials such as starch, glucose, milk powder, antibiotics, vitamins, Chinese medicine extracts, yeast, enzyme preparations, etc;
Minerals and building materials: clay, kaolin, diatomaceous earth, graphite, metal hydroxides (such as aluminum hydroxide) and other minerals with high water content or easy to agglomerate;
Agriculture and biomass: organic materials such as feed additives, plant fibers, sludge, distiller's grains, coffee grounds, etc., drying and reducing microbial activity.