LIST
PRODUCTS
Contact us
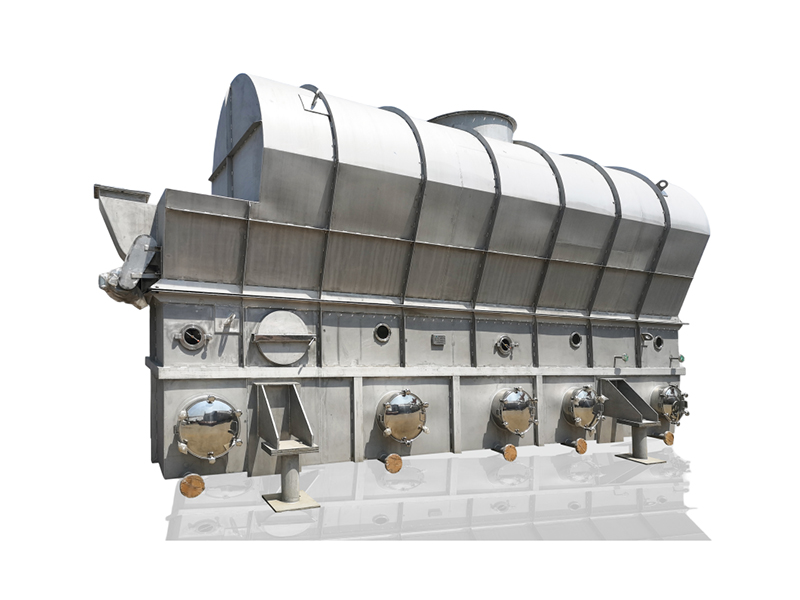
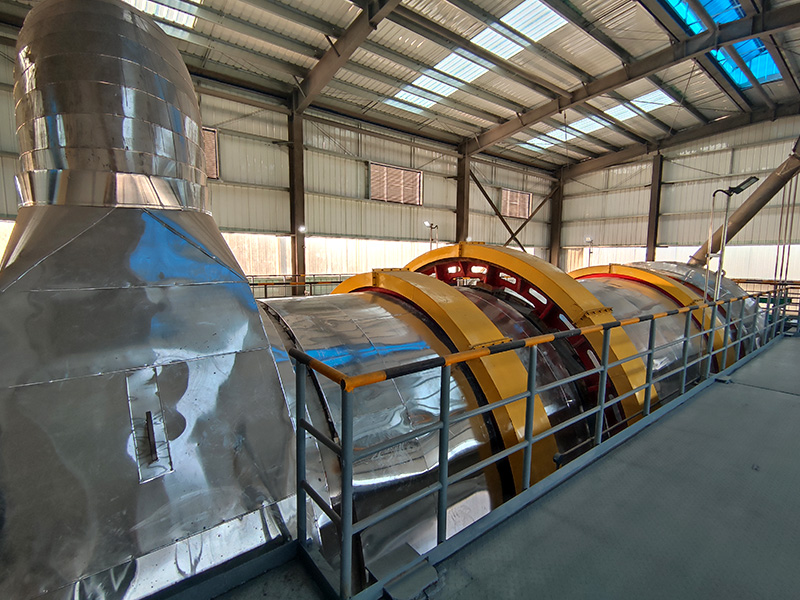
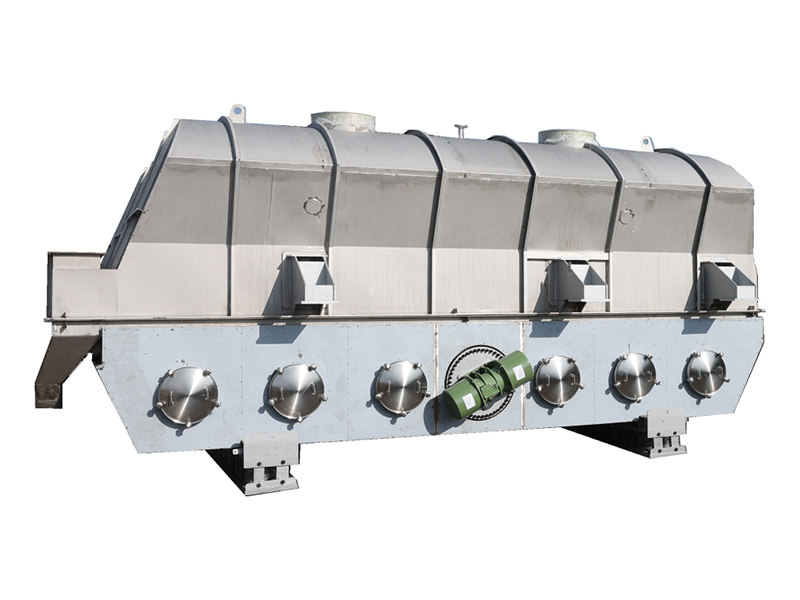
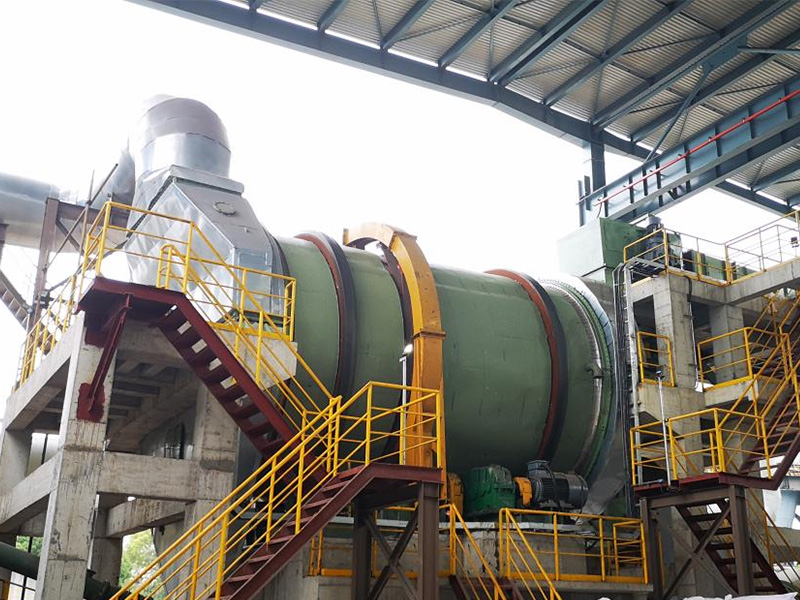
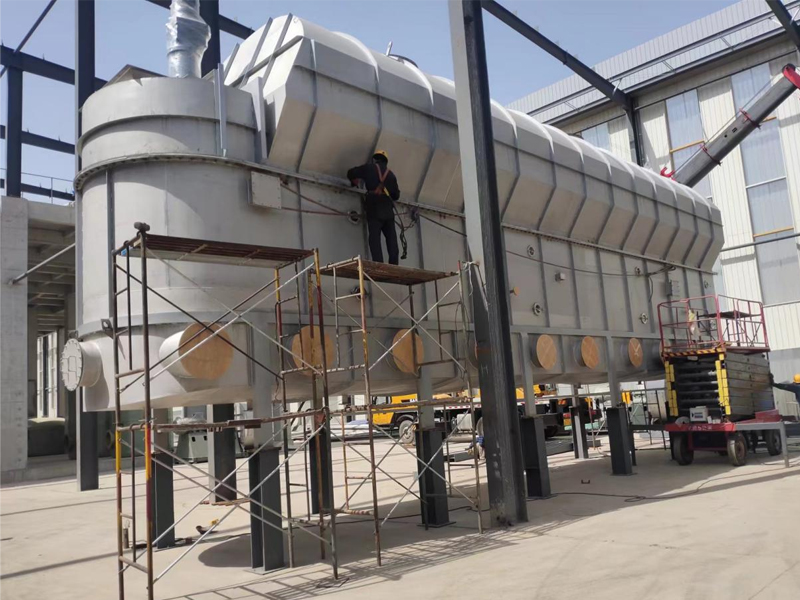
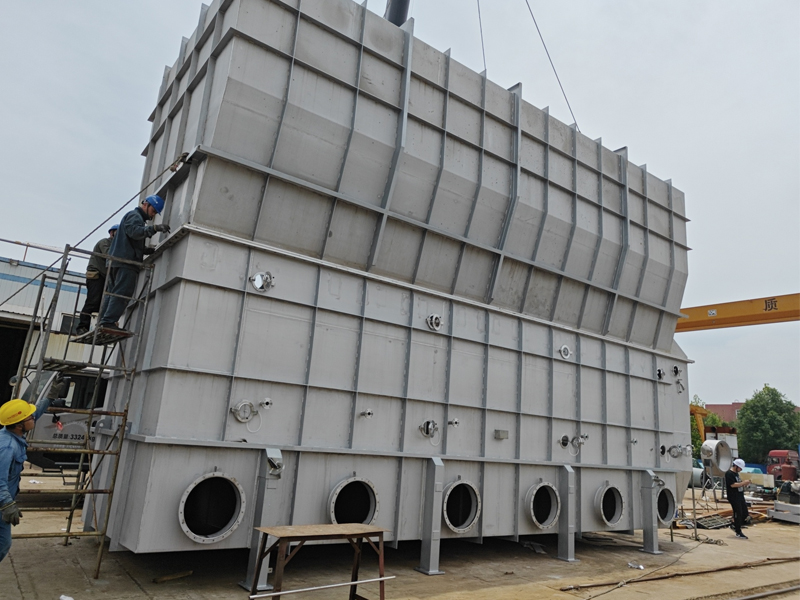
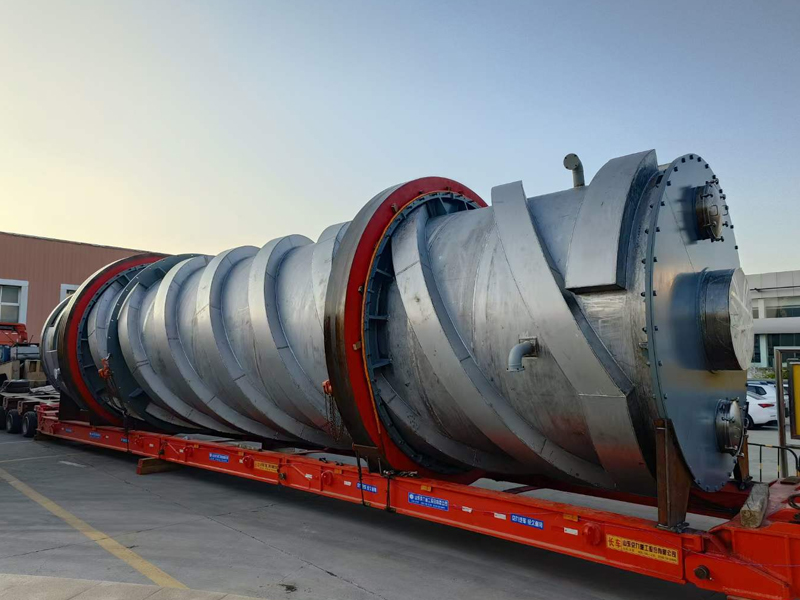
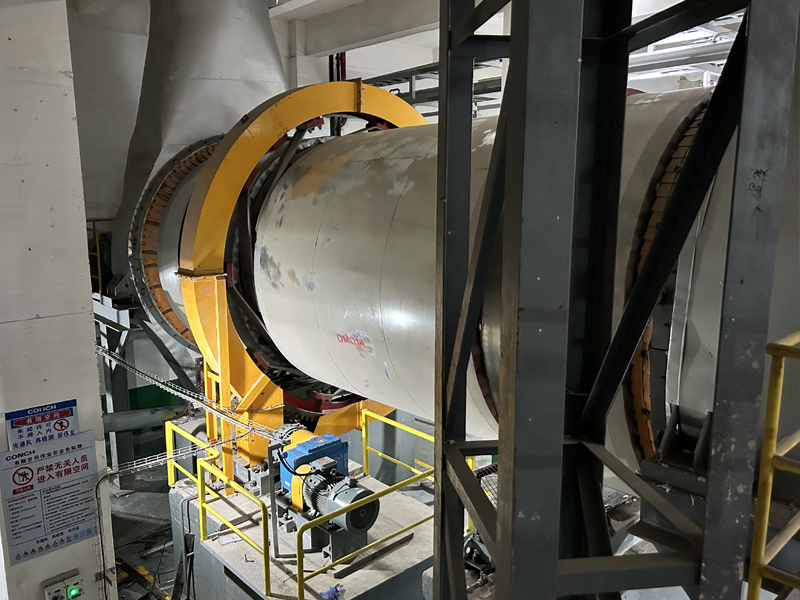
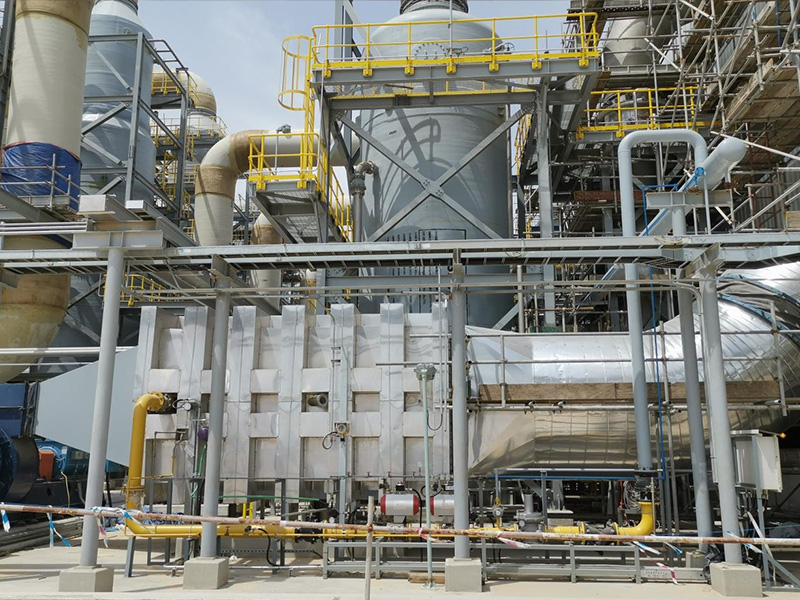
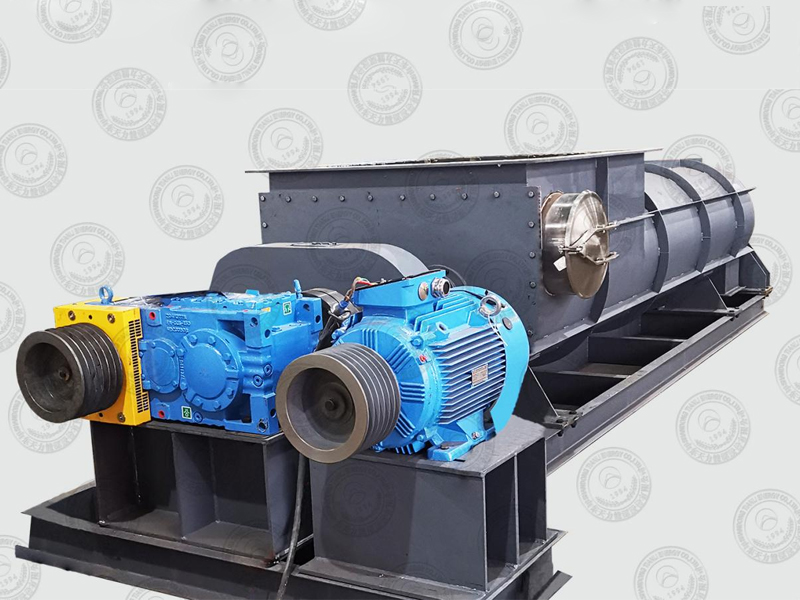
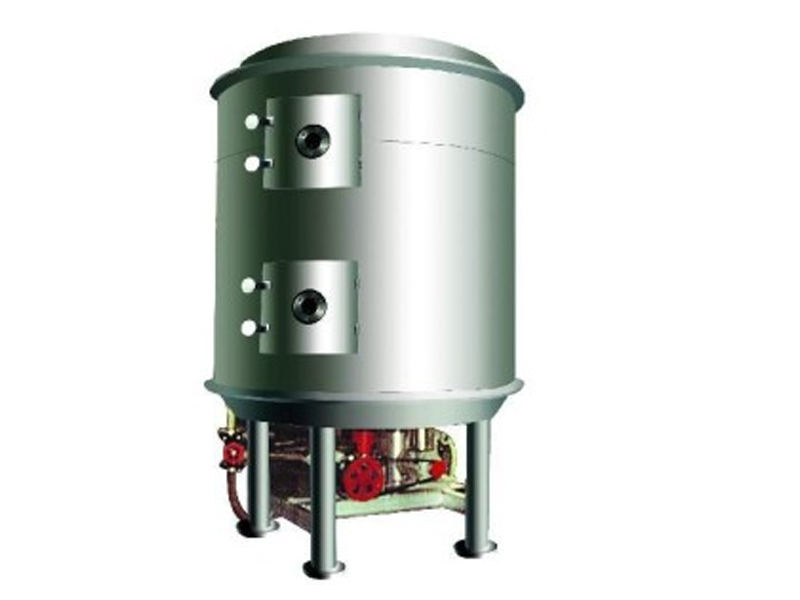
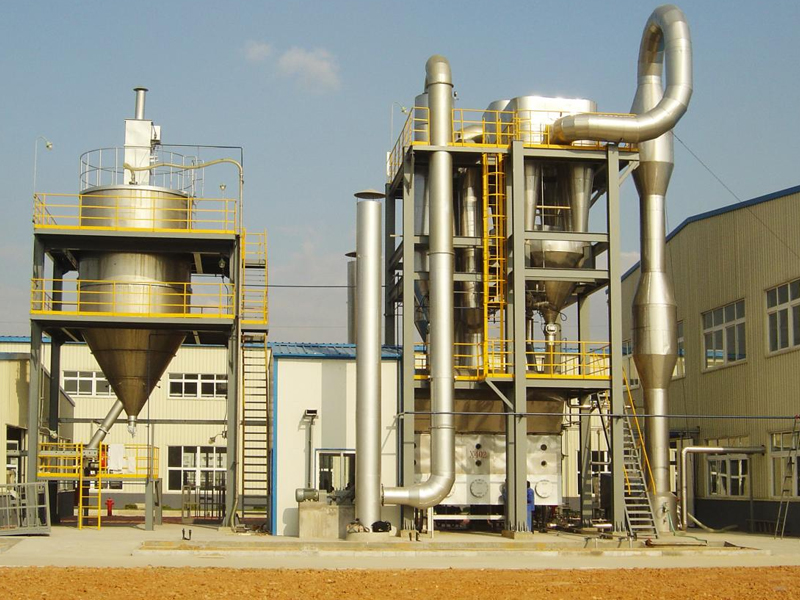
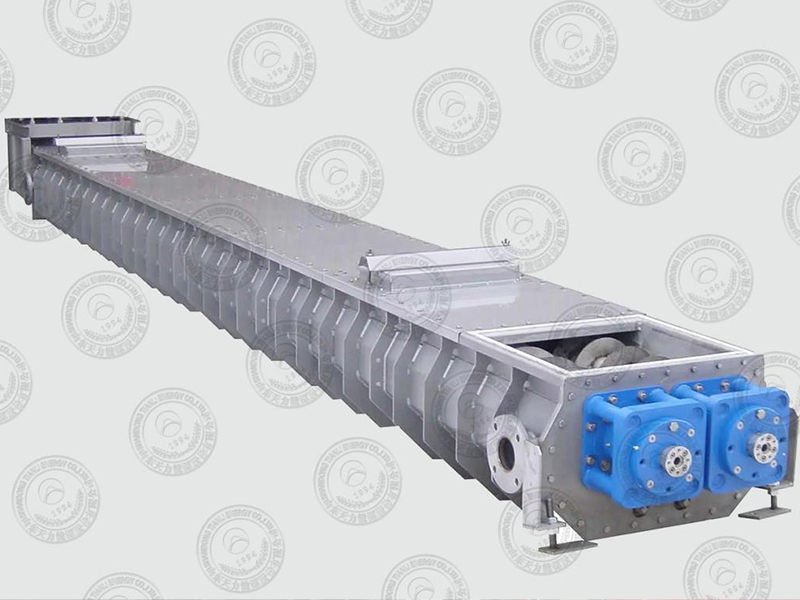
Lined Coating Fluid Bed Dryer
- Tianli
- China
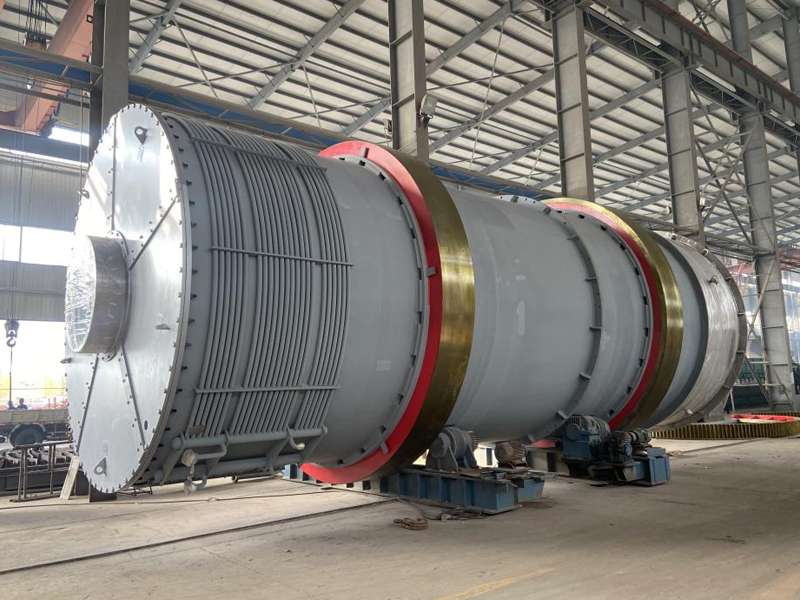
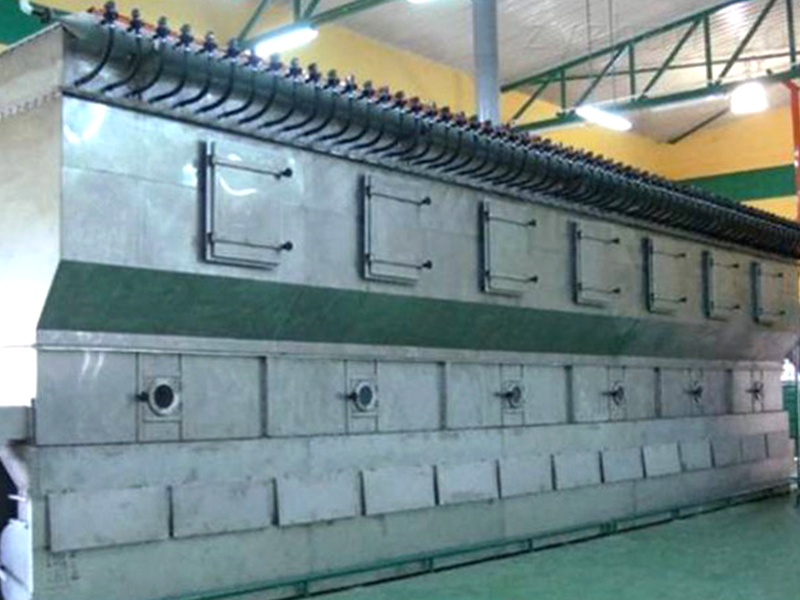
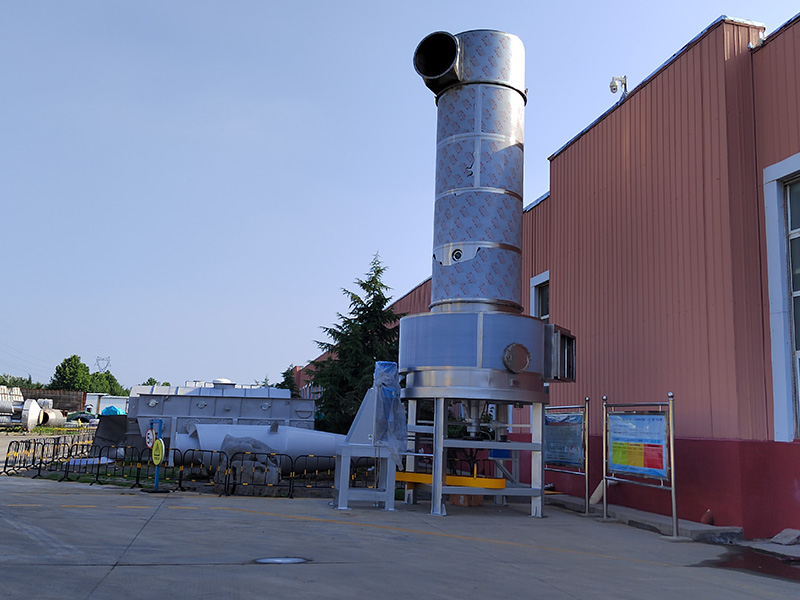
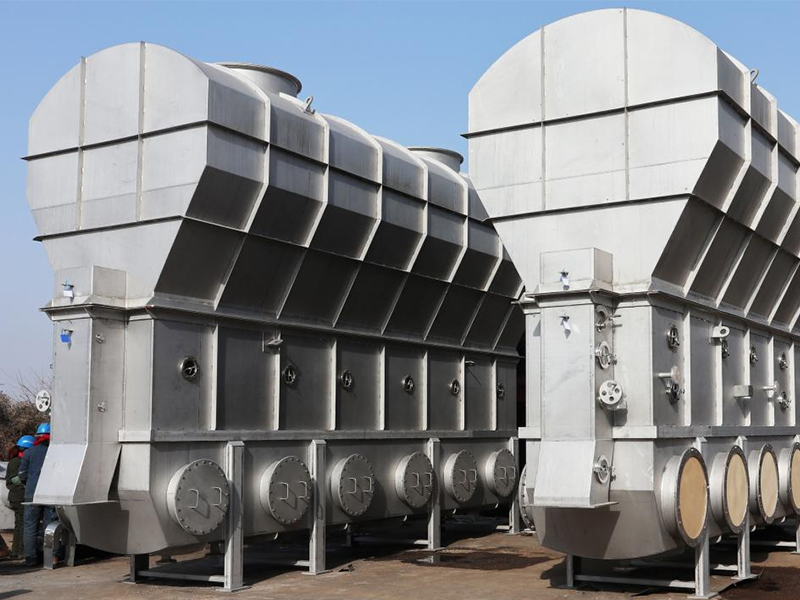
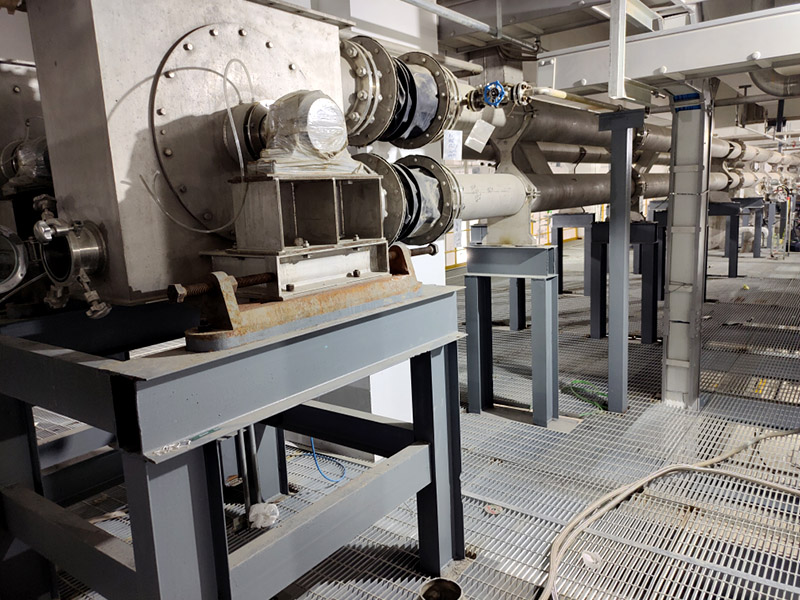
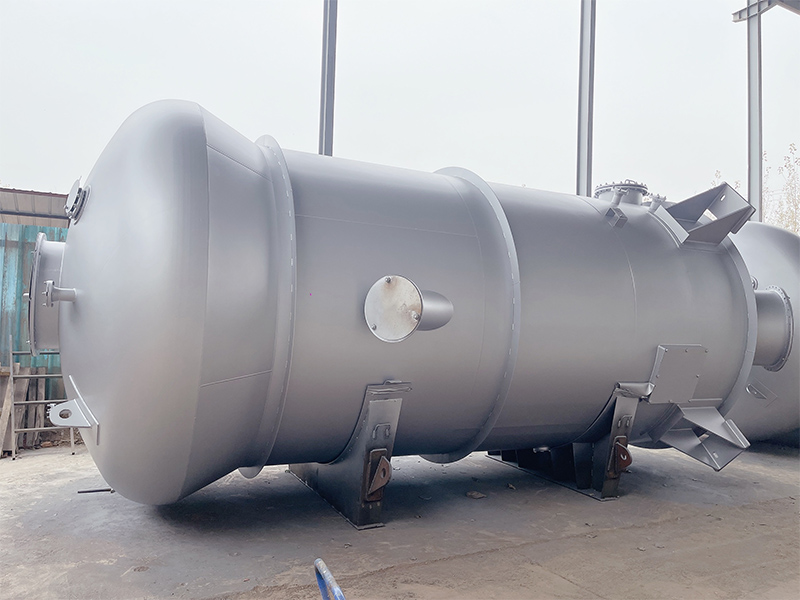
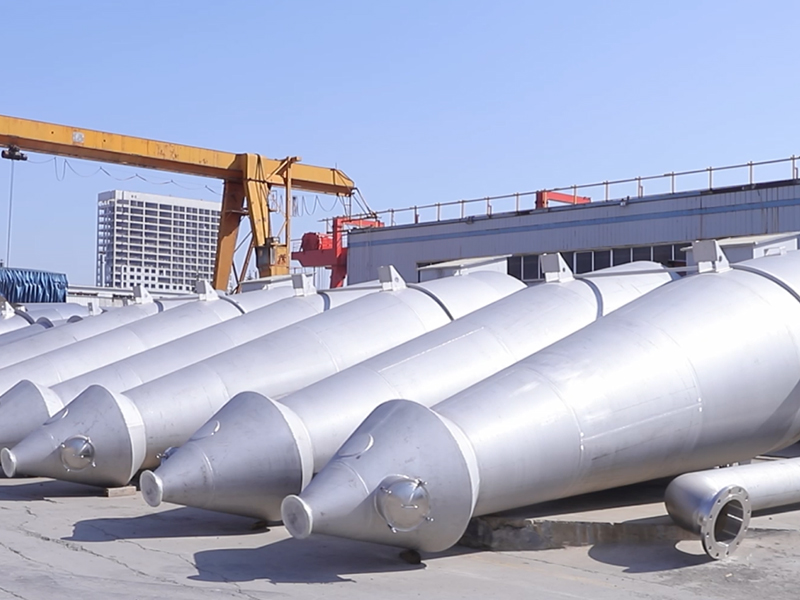
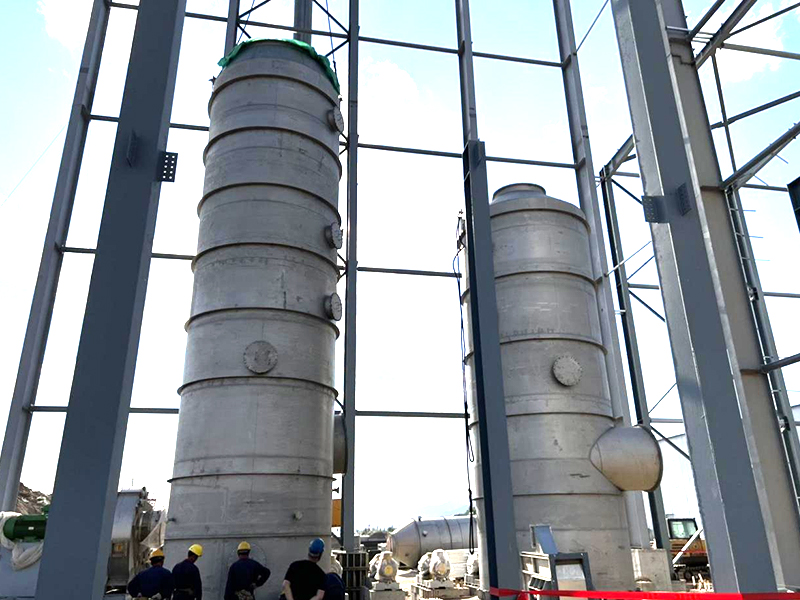
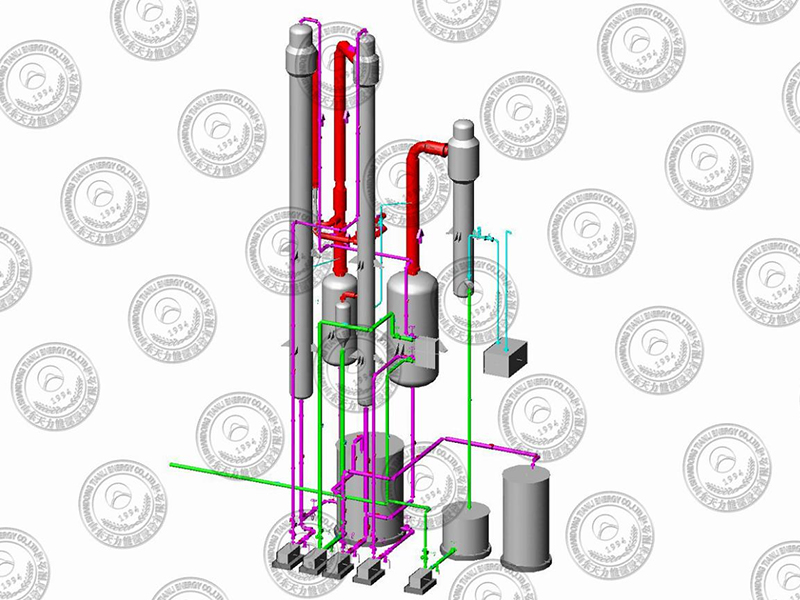
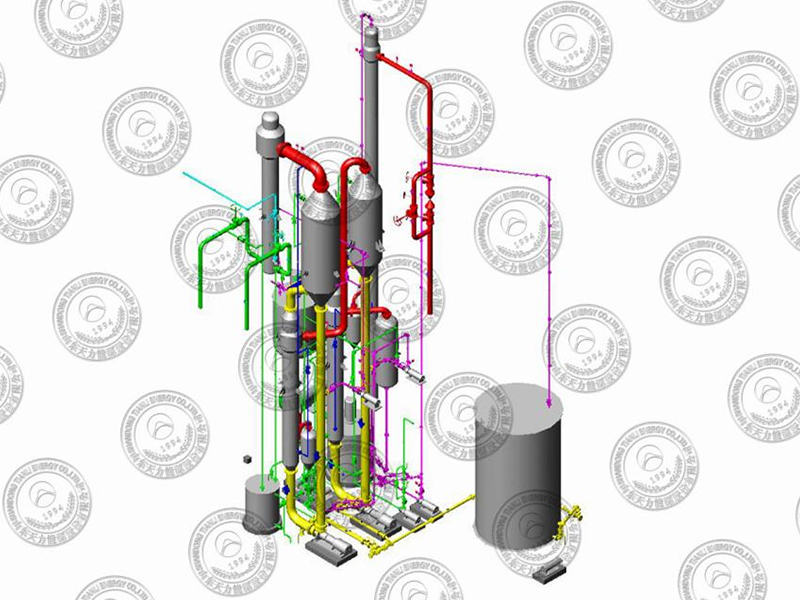
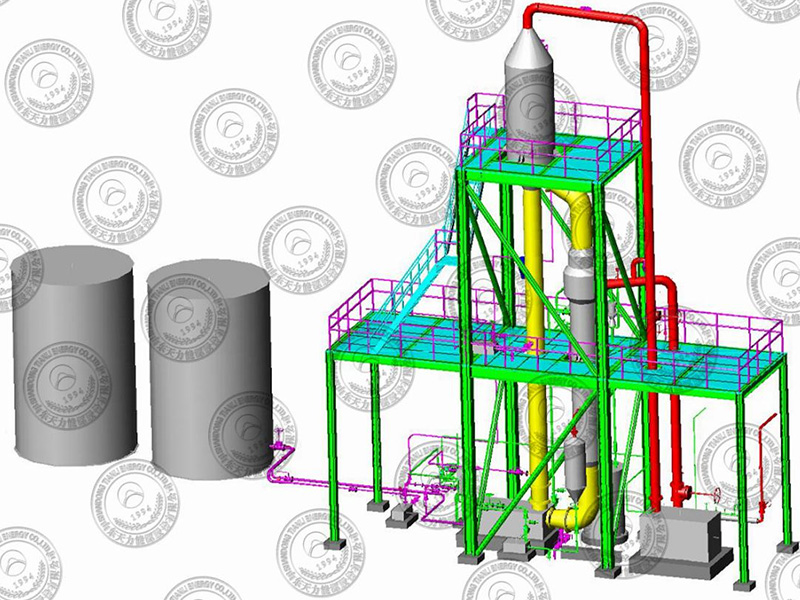
Equipment Structure
Equipment Structure
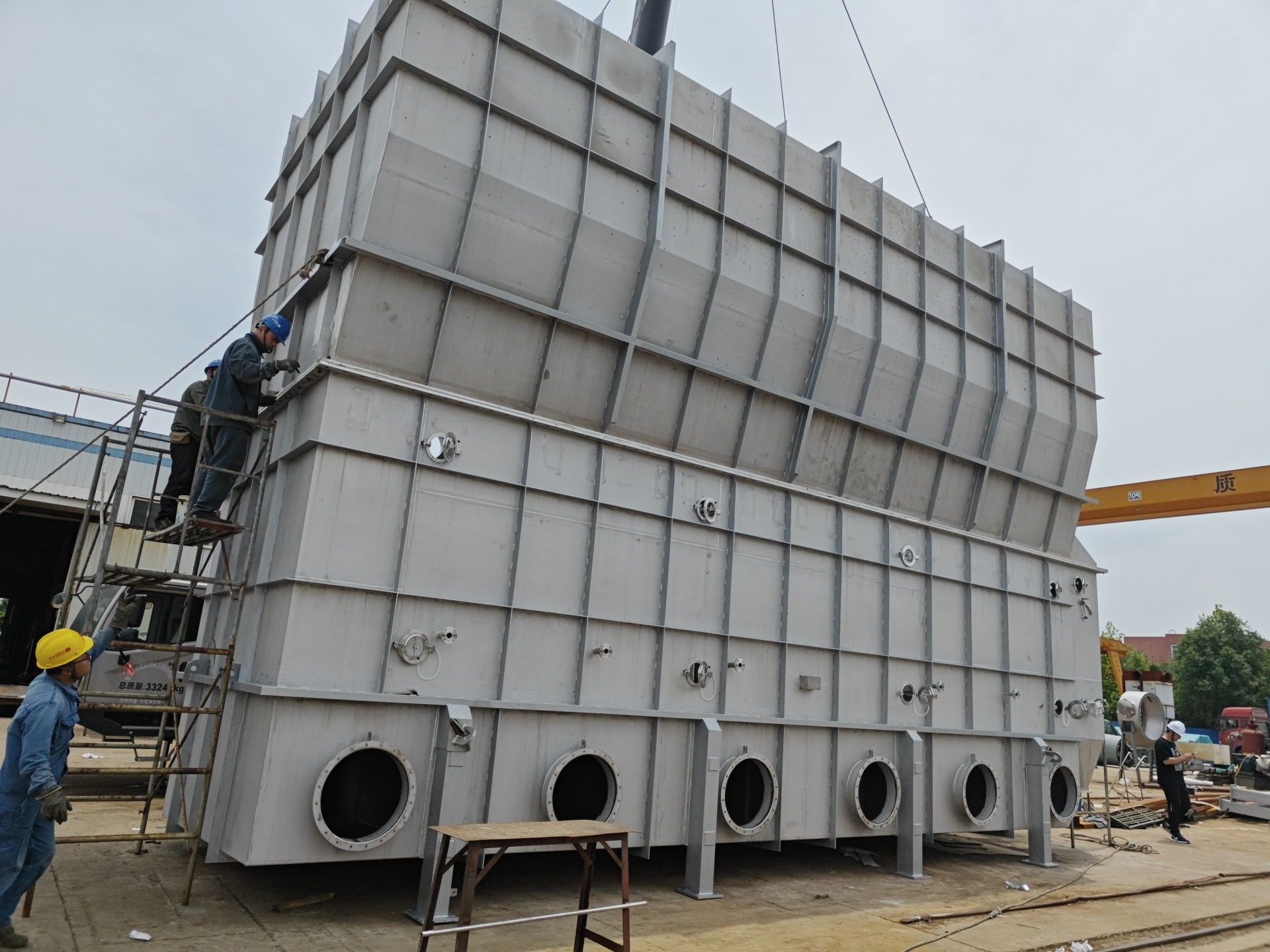

During the design and manufacturing process of the fluid bed dryer, Tianli sprays coatings inside it, mainly to resist wear, prevent corrosion, avoid material adhesion, and meet specific hygiene requirements (such as food and pharmaceutical industries). Common coating types include:
Wear-resistant polyurethane coating:
Advantages: This is one of the most widely used coatings for fluid bed dryer. It has excellent wear resistance and can effectively resist the scouring and impact of particles. It has good elasticity and excellent impact resistance. It also has relatively good chemical resistance (depending on the specific formula). It can be formulated into different colors. It is relatively convenient to apply (can be sprayed or brushed).
Application: It is widely used in drying applications with severe wear such as chemicals, minerals, and plastic particles. There are FDA/USP Class VI certified polyurethane coatings specifically for the food or pharmaceutical industries.
Wear-resistant epoxy coating:
Advantages: High hardness, strong adhesion, excellent chemical corrosion resistance (especially acid, alkali, and solvent resistance), and good wear resistance (usually slightly inferior to top polyurethane, but still excellent). Disadvantages: Compared with polyurethane, it has slightly worse toughness and may have slightly lower impact resistance.
Application: It is particularly suitable for fluid bed dryers that handle corrosive chemicals, solvents, or acidic and alkaline materials. There are also epoxy coatings that meet food/pharmaceutical hygiene standards.
Ceramic coating (such as aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, chromium oxide base):
Advantages: extremely high hardness, excellent wear resistance, high temperature resistance, excellent corrosion resistance (strong inertness), very smooth surface, not easy to stick. Disadvantages: high cost, complex construction process (often requiring high temperature sintering or thermal spraying), brittle coating, relatively poor resistance to thermal shock and mechanical impact. Difficult to repair.
Application: used in extreme wear, high temperature or strong corrosion environment. For example, drying of certain metal powders, catalysts, high hardness minerals, etc. It is often used in the form of wear-resistant ceramic sheets or integral ceramic linings.
High-performance non-stick coating or lining layer (such as modified PTFE/polytetrafluoroethylene, PFA, etc.):
Advantages: extremely low surface energy, excellent anti-stick performance, easy to clean, excellent chemical resistance.
Disadvantages: pure PTFE has poor wear resistance and usually needs to be compounded or modified with other resins (such as polyimide, PEEK) to improve wear resistance and adhesion. There is an upper limit to temperature resistance.
Application: Mainly used to process materials that are easily melted or softened by heat or have high viscosity (such as certain polymers, food raw materials, sugar-containing materials) to prevent the materials from accumulating and agglomerating on the wall.
Other special coatings: Elastomer coatings (such as rubber linings): mainly used for corrosion resistance and impact absorption, but the wear resistance is not as good as polyurethane/ceramic, and it is not suitable for high temperatures.
Glass flake coating: glass flakes are used to enhance permeability resistance and corrosion resistance. They are often used in highly corrosive environments, but the wear resistance is average.
Key factors when selecting a coating:
1. Material properties: hardness, particle shape, density (affecting impact force), corrosiveness (acid, alkali, solvent), viscosity, temperature, whether it is required to be non-toxic/meet hygiene standards;
2. Operating conditions: operating temperature, humidity, pressure, gas composition (such as oxygen content), cleaning method (CIP/SIP);
3. Abrasion degree: air flow velocity, material loading, fluidization intensity;
4. Cost budget: initial cost and maintenance cost;
5. Construction requirements: surface treatment level (such as sandblasting Sa 2.5), curing conditions (normal temperature/high temperature), construction difficulty.
Tianli has rich experience in various coating forms through 30 years of drying engineering accumulation. The most common is the high-performance wear-resistant polyurethane coating, which strikes a good balance between wear resistance, chemical resistance and cost. For highly corrosive environments, wear-resistant epoxy coatings are the first choice. In the face of extreme wear or high temperatures, ceramic coatings or wear-resistant ceramic linings are the solution. When dealing with sticky materials, high-performance non-stick coatings (modified PTFE, etc.) are necessary. The food and pharmaceutical industries must choose certified coatings that comply with relevant hygiene regulations and are easy to clean.